As a dental practice owner in the U.S., you are already aware that the story of clinical skills and patient care does not end there. The financial operations behind every healthy smile include income tracking, insurance payments, payroll, tax compliance and so on. Without strong bookkeeping for dental practices, your financial picture can become foggy, and your growth stalls since decision-making will get harder.
In this post, you will learn everything that you would require to work clean, compliant and growth-oriented bookkeeping in your dental practice, including the basic building blocks and the advanced techniques, as well as the pitfalls to be aware of. You will also learn when to consider outsourcing your bookkeeping for dental practices. This guide will help you find your way to financial health regardless of whether you are the dentist-owner, office manager, or financial lead.
Let’s get started.
What is Dental Bookkeeping?

At its core, dental bookkeeping is the specialised accounting function tailored for dental practices. It involves recording, organising, and managing all financial transactions that a dental clinic undertakes. This includes:
- Monitoring revenues from patients (insurance payments, patient payments, co-payments)
- Managing and controlling operating expenses (rent, utilities, supplies, lab fees).
- Reconciling accounts and bank statements.
- Staff/payroll remuneration.
- Dental equipment depreciation.
- Handling accounts receivable (AR) and accounts payable (AP).
- Development of financial statements (profit and loss, balance sheet, cash flow).
Since dental practices involve insurance, reimbursements, and complicated billings, specific domain knowledge is required in dental bookkeeping than in generic bookkeeping. It’s more than just numbers; it’s a financial structure built around how dental practices work.
Within dental bookkeeping, you will sometimes see terms like ‘dental practice accounting’ (which covers broader financial strategy and reporting) and ‘dental bookkeeping software‘ (tools to perform the bookkeeping functions). Together, they ensure your practice’s financial engine runs smoothly.
Why Bookkeeping is Essential for Dental Practices?
Proper bookkeeping is more than regulatory housekeeping; proper bookkeeping is the basis of financial clarity, efficiency and growth. Reasons why it is important:
Accurate Financial Visibility
You cannot manage something that you cannot measure. Accurate bookkeeping provides you with a real-time picture of revenue, expenses, profit and cash flow.
Better Decision-Making & Growth Planning
Reliable data helps you with effective forecasting, budgeting and planning for the expansion or purchasing of new equipment.
Tax Compliance and Minimisation
The tax code of the U.S. provides deductions and credits; however, only in cases where your records are clean. Bad bookkeeping usually results in missed tax opportunities or IRS fines.
Operational Efficiency
Process automation, detecting errors at initial stages, and optimisation of workflows can help minimise the administrative load and release the personnel to work with patients.
Audit Readiness & Risk Mitigation
Solid records are required in insurance audits, state compliance audits or internal audits. Clean books protect you against regulatory risk.
Valuation & Exit Planning
If you ever sell or merge your practice, potential buyers will scrutinise your financials. Well-maintained books increase your valuation.
In short: bookkeeping isn’t optional — it’s strategic.
Key Components of Dental Bookkeeping
Certain key elements must be addressed to make bookkeeping right. The following are the building blocks that cannot be skipped:
1. Chart of Accounts Designed for Dental Practices
Apply a dental-specific COA (Chart of Accounts) which distinguishes clinical revenue (procedures, lab fees) and administrative revenue and distinguishes costs such as dental supplies, lab expenses, staff wages, and FFS (fee-for-service) vs. insurance revenue.
2. Revenue Tracking & Recognition
Separate patient payments and insurance reimbursements. Reconcile the discrepancy or underpayment. Make sure that you record revenue in the period (accrual vs. cash basis).
3. Expense Management & Categorisation
Maintain a record of all expenses: rent, utilities, instruments, lab costs, sterilisation, office supplies, software licences, etc. Categorise all costs in great detail so that you can analyse cost drivers.
4. Accounts Receivable & Collections
Track unpaid insurance claims and balances. Send statements on time, follow up on delinquencies and use collection practices.
5. Bank & Credit Card Reconciliation
Monthly reconciliation is non-negotiable. Match your bank/credit card statements to your books and address discrepancies.
6. Payroll Management
Dentists, hygienists, assistants, and front-desk staff all require proper payroll with withholding, benefits, overtime, and tax filings. This is often one of the more complex areas in dental payroll management.
7. Depreciation and Asset Accounting
Dental practices invest significantly in equipment (X-ray machines, chairs, sterilisers). You must depreciate them correctly and reflect their value on balance sheets.
8. Cash Flow Management
Follow cash receivables and receivables, and audit timing discrepancies (e.g., many insurance payments are lagging behind services). Maximising your cash flow would make sure that you are able to meet commitments.
9. Financial Reporting & Analytics
Generate profit and loss, balance sheets, budgets, variance reports, and KPIs. It is also important to monitor key metrics like collections ratio, overhead percentage, production per provider, and net income margins.
Common Mistakes US Dentists Make in Bookkeeping and How to Avoid Them
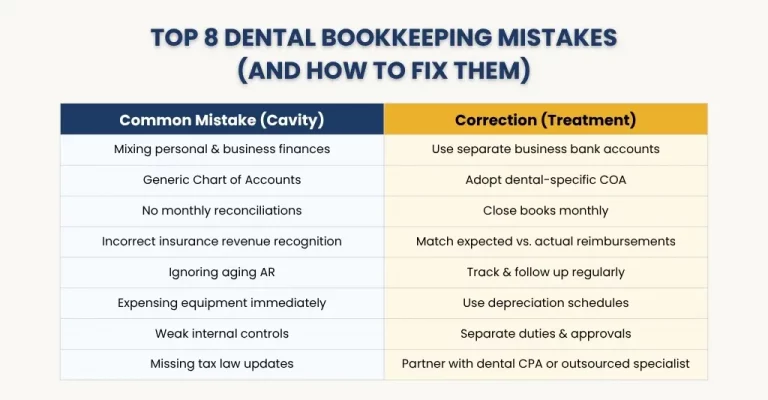
Even experienced practitioners make bookkeeping mistakes that cause costly consequences. Here’s what to watch for — and how to correct them:
Mixing Personal and Practice Finances
Using the same account for personal and business transactions confuses your books and may expose you to audit risk. Always maintain a separate business banking account and credit card.
Using a Generic Chart of Accounts
If your COA isn’t tailored to dental, your reports won’t show the insights you need. You’ll lose nuance around clinical vs. administrative costs.
Neglecting Reconciliations / Delaying Book Closes
Letting errors accumulate instead of reconciling monthly leads to compounding mistakes. Practices should “close their books” monthly.
Improper Revenue Recognition / Insurance Mismatch
Failing to reconcile the difference between expected insurance reimbursement and actual paid amounts leads to overstatement of revenue.
Ignoring Aging AR / Bad Debt Provisions
Letting unpaid balances pile up without reserves distorts true profitability.
Overlooking Depreciation or Capital Expense Handling
Expenses incurred towards equipment purchases are treated as immediate expenses rather than depreciation and are also misstated.
Weak Internal Controls & Fraud Exposure
Incorrect or no separation of duties, inadequate oversight or oversight of any form of tracking can result in internal theft or data corruption.
Failing to Stay Up-to-Date with Tax Law
Failing to take into consideration IRS or state tax code changes costs you deductions or imposes penalties.
These can be avoided by developing structured processes, being consistent and using checks and balances.
Time is running out to fix your books — avoid costly penalties and stay audit-ready by booking your Dental Accounting review today!
Essential Tools & Technology for Streamlined Dental Bookkeeping
Modern technology today is a disruptor. With the right tools and domain knowledge, an accurate and faster bookkeeping process becomes a reality.
- Cloud-Based Accounting Software: QuickBooks Online, Xero, or dental-specific accounting packages – safe, secure and automatically synced – will get rid of paper chaos.
- Dental Practice Management / Billing Systems: Patient record management systems, appointment scheduling systems, and billing code generation systems that can be incorporated into your accounting.
- Automation & AI Tools: Receipt scanning, automatic categorisation, and bank feed reconciling tools.
- Reporting Dashboards & BI Tools: Live dashboards displaying your KPIs, financial trends and metrics.
- Payroll & HR Software: Tools that automate withholding, benefits tracking, and payroll tax compliance.
- Backup & Security Systems: Because patient and financial data are sensitive, ensure HIPAA-level or industry-standard encryption and data redundancy.
- Mobile Apps & Cloud Access: Access your practice’s financials from anywhere, anytime — useful for multi-location practices.
When combined, these systems give you a robust, scalable, and low-error bookkeeping ecosystem.
Best Practices to Maintain Organised Financial Records
To ensure your bookkeeping stays clean and reliable, adopt these practices consistently:
- Establish a Monthly Close Routine — Reconcile bank accounts, credit accounts, AR, AP, depreciation and check the variances.
- Use a Dental-specific Chart of Accounts – Customised to your practice.
- Train Staff on Documentation & Coding – Front office staff must correctly code services, capture payments, and manage insurance claims.
- Document All Policies & Processes — Standardise routines for recording, approvals, and reconciliations.
- Review Financial Reports Monthly — Do not wait till year-end; analyse P&L, balance sheet and KPIs.
- Monitor KPIs — Measure KPIs such as collection ratio, overhead as a percentage of revenue, staff productivity, return on capital, etc.
- Budget & Variance Analysis — Establish monthly and yearly budgets and compare actuals and plans.
- Maintain Audit Trail — All of the transactions must be trackable (invoice, receipt, approval).
- Retain Records Properly — Retain tax records, financial reports and supporting documents where necessary and required.
- Regularly Update Software & Security — Keep your software and data protected.
When you respect these practices, financial chaos becomes a thing of the past.
Tax Planning and Compliance Strategies for US Dental Practices
Dental practices must navigate complex U.S. tax rules. Here’s how to stay compliant and optimise tax outcomes:
1. Understand Your Tax Structure
The type of business structure you have impacts the taxation of income, deductions and distributions of your business, which include: Sole proprietorship, S-corp, LLC and corporation. Consult a dental-specialized CPA.
2. Track All Deductible Expenses
Track all deductible expenses, including dental supplies, additional education, professional subscriptions, insurance, business travel, amortisation and depreciation.
3. Section 179 & Bonus Depreciation
You could possibly deduct equipment acquisitions right away under Section 179 or comply with bonus depreciation regulations; however, your bookkeeping has to capture the correct information of assets.
4. Retirement & Health Plans
Strategically reduce taxable income using 401(k), SEP IRA or other retirement plans.
5. Estimated Tax Payments
Dentists are supposed to pay quarterly estimated taxes to evade underpayment fines.
6. State & Local Tax Compliance
Keep up to date on state-imposed dental tax requirements, licensure, sales tax (where applicable), and local business tax requirements.
7. Audit Readiness & Documentation
Keep records in order to be able to justify expenses asserted in case you are audited.
8. Succession & Exit Tax Planning
If you plan to sell or transition your practice, your books must stand up to scrutiny and valuation standards.
By aligning your bookkeeping with tax strategy, you maximise deductions, minimise liabilities, and maintain compliance.
Advanced Tips for Dental Practice Financial Success
Once the basics are solid, you can push into more strategic territory:
- Perform Profitability Analysis by Procedure: Know which treatments are most profitable.
- Utilise Benchmarking: Compare your performance data (overhead percentage, production per provider) to industry standards.
- Implement Rolling Forecasts: Other than the fixed budgets, apply rolling forecasts so as to respond to change.
- Manage Working Capital Proactively: Be Proactive. You can negotiate with suppliers on payment terms, manage AR collections, and optimise inventory.
- Leverage Financing Strategically: In case of expansion or equipment, select the method of financing that will not cripple cash flow.
- Adopt Multi-location Consolidated Reporting: In case you are operating in multiple locations, consolidate your accounting system and reporting.
- Continuous Staff Training & Incentives: Educate your front office and financial management to code, collect and control expenses.
- Use KPI Dashboards: Track such measures as collection percentage, Days in AR, overhead ratio, and EBITDA margin.
- Integrate Practice Management with Accounting: Minimise redundancy in entering and reconciliation problems.
- Scenario Planning: Run what-if models: what if patient load reduces, insurance payback slows down, or a location is shut down?
These advanced strategies let you not just stay afloat but also accelerate growth and resilience.
Outsourcing vs In-House Bookkeeping: Choosing the Right Approach
One of the biggest decisions you’ll make is whether to keep bookkeeping in-house or outsource to a specialist like E2E Accounting. Each approach has pros and cons:
In-House Bookkeeping Pros
- Direct control over staff and processes
- Instant access to internal personnel
- Deep institutional knowledge
In-House Cons
- Higher fixed costs (salary, benefits, training)
- Risk of turnover or error
- Scalability challenges during growth or busy periods
Outsourced Dental Bookkeeping Pros
- Access to experienced, dental-specific accounting professionals
- Lower overhead and variable cost structure
- Scalability, flexibility (ups and downs)
- Inbuilt checks and levels of review.
- Newest compliance awareness and programme.
Outsourced Cons
- Fewer day-to-day controls (but with effective communication, this can be allayed)
- Vendor requirements (data security, reputational risk) are high.
Choosing the appropriate approach will be based on such factors as the size of the practice, the volume of transactions, complexity, staff resources, growth objectives, and risk tolerance.
A hybrid business model is highly effective in the context of many dental practices: the basic bookkeeping is handled internally, and the specialised work or audit is outsourced to a third party.
Outsourced dental bookkeeping with domain-specific specialists can be a significant factor in your favour, should you need to scale, reduce risk, and ability to grow financially without straining your team.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
What is “Bookkeeping for Dental Practices”?
It’s the specialised process of capturing, categorising, and managing all financial transactions (income, expenses, payroll, AR/AP) uniquely structured for dental clinics.
Why can’t I use generic bookkeeping for my dental office?
The bookkeeping in generic form is usually not subtle; it lacks insurance reimbursements, dental-specific expense items, and complicated revenue recognition that are found in dental practices.
How often should I reconcile accounts and close books in a dental practice?
Monthly is standard. Some practices do weekly reconciliations, especially for bank/credit card accounts, to catch errors quickly.
Can outsourcing dental bookkeeping help with U.S. tax compliance?
Absolutely. An excellent outsourced partner can make sure that the records can be used to claim tax deductions, settle the state and federal requirements, provide an audit trail, and be in compliance with the IRS requirements.
What software is best for dental bookkeeping?
It will rest upon your scale and integration requirements. Favorable alternatives are QuickBooks Online, Xero or accounting solutions specific to the dental industry. It is important to integrate practice management software and have automation features.
When should a dental practice consider outsourcing bookkeeping?
Whenever you are dealing with more transactions or more complexity, you are overwhelmed by your staff, or you desire to be more accurate, develop strategic insights, or grow without adding internal personnel.
Conclusion
Running a dental practice means juggling patient care, operational logistics, and above all, your financial health. Dental practice bookkeeping is the foundation upon which all other decisions are made, including staffing and expansion, as well as tax planning and profitability.
You can be strategic by learning to master the most important elements, namely, the tracking of revenue, expense control, cash flow management, reporting, and compliance. These pitfalls should be avoided, modern tools taken, disciplined practices thought of, and, when necessary, you should use outsourced dental bookkeeping to provide both accuracy and size to your practice.
At E2E Accounting, we understand the unique financial challenges dentists face. We combine domain expertise with powerful accounting tools to help you maintain sound books, optimise taxes, and gain meaningful financial insights — so you can focus on what truly matters: your patients and your practice growth.
Let us partner with you to turn your financial operations into one of your greatest assets.

